We have all heard of how Forensic Dentistry has helped in the identification of burnt victims and also victims with bite marks. Explain more about these and describe how is Forensic Dentistry could be useful in the identification of murder victims?
Forensic odontology, also known as forensic dentistry, is the study and the use of dental knowledge to deal with legal issues. It involves the proper collection, handling, examination, and evaluation of dental evidence.
Forensic odontology works on the principle that no two people have exactly the same dental imprints. Extractions, fillings, chipped, gapped, or closely spaced teeth can all be used to identify who the teeth marks are from. Some teeth may even be twisted or tilted. Even with individuals who have had their teeth straightened through the use of braces, there will be some distinctive features that can be used to identify them based on their dental work.
.jpg)

The most common task in forensic odontology is to identify the deceased. A specialist will be called in to compare the deceased's most recent dental records to the teeth of the corpse. If there are no dental records available, the forensic odontologist will prepare a profile of the deceased based on their teeth. The identification can be done by using dental records including radiographs, ante-mortem (prior to death) and post-mortem photographs and DNA.

Postmortem Odontogram
The forensic dentists are responsible for six main areas of practice:
- · Identification of found human remains
- · Identification in mass fatalities
- · Assessment of bite mark injuries
- · Assessment of cases of abuse (child, spousal, elder)
- · Civil cases involving malpractice
- · Age estimation
There are a few means by which a forensic dentist can use to investigate on a crime case, which includes identification of human remains, assessment of bite-mark evidences, age estimation, DNA-sampling, radiology and forensic odontology.
Identification of human remains can help in age and gender estimation, for example with the analysis of cranial and pubic suture closure, radiographic aging of the femur and articular surface, patterns of tooth eruption and tooth wear.
Bite-mark evidence is a good source to aid in the identification of criminals. The bite-marks can be picked up from either the victims or the criminals, or even food at the crime scenes. It is possible to identify specific types of teeth by their class characteristics. For example, incisors produce rectangular injuries and canines produce triangular injuries. A dental impression can be made of any suspect and be compared to the bite-marks. However, there is a significant rate of false identification using just bite-mark evidence.

The extraction of mtDNA from tooth pulps for DNA-sampling and criminal identification is one of the most commonly used and most accurate method in forensic dentistry. This is done with the use of a technique known as the nuclear DNA typing and amplification of the DNA via polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Other than the tooth pulps, DNA samples can also be acquired from the gingiva, saliva and the hair.
In radiology and forensic odontology, any bone loss, caries, crowns, fixed bridges and tooth restorations can be revealed from the radioopacity and radiolucency of the radiographs. Because of the high temperature resistance of enamel, which can hold up to 1000 degree Celsius of heat waves, tooth identification with radiographs and forensic dentistry can come in handy in devastating disasters such as air crashes or any fire accidents.

Antemortem image of frontal sinuses.

Postmortem view of the frontal sinuses in the previous image. Dehydration may have accounted for the relative clarity of the film as compared with the antemortem film in the previous image.

This radiograph of the maxillary sinus shows another site for analysis when the dentition is missing. (From the private collection of Phil Levine, DDS, Pensacola, Fla.
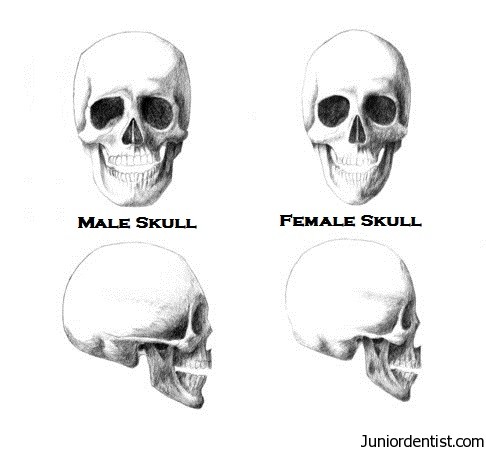
Is a male human skull different from that of a female? If yes, how?
The skull has features that can determine sex, but how? At young age, the sex-related skull features are less distinct and usually more difficult to interpret. However, as they reach puberty and go through sexual maturation, the skull will become more defined and hence sex will be more detectable. It is very important in forensics investigation to differentiate the differences between male and female skull which will be discussed below.
The male and female skull are differentiated by characteristics like size, weight shape and etc. The Table 1.0 below shows the characteristics of the skull.
ps: refer to Figure 1.1 and Figure 1.2

Figure 1.1

Figure 1.2

Table 1.0
In a nutshell, the male human skull is different from a female human skull. There is a problem determining sex using skeleton remains especially when only fragments of body are found, thus, the forensic odontologist may assist other experts to determine the sex of victims by using skull and teeth. Features like morphology of the tooth and skull has important characteristics for male and female sexes. This plays a very important role in human identification in Forensic odontology by investigating the aspects of dental evidence like the skull and teeth to establish the sex of victims with bodies beyond recognition due to major mass disaster. Besides determining the sex using skeleton, age also can be determine from skull and teeth.
However, new developments like PCR amplification can accurately determine the sex of remains.
From the story above so far, how many victims are there? Explain.
BUT......
So far, there is insufficient information to determine the exact number of victims. However, we are assuming that all the bony pieces found belong to one person only. That is, if all the pieces found were to be assembled, we would get one human skull.
Further excavation must be done to determine for sure if there is more than one victim. At this stage it is also not possible to determine the gender, ethnicity and age of the victim.
Over time, certain changes might occur to the remains. A depression of the skull/broken bones could indicate death due to skull fracture but again, decomposition factors such as weather, soil chemical components, scavengers and insects must be taken into consideration. Or, the chin of a female (more rounded) can be mistaken for that of a male (more square) after decay over a long period.
The age can be determined by examining bone sizes and fusions/sutures. With age, joints or fontanels also change in size. Bone loss is significant of advanced age. Bone ossification examination also helps. Teeth erupt in a certain order and that also can greatly help determine the age. Additional information comes from examining the degree of root development deep within the jawbone. If wisdom teeth are present, individual was above 18. Finally, the microscopic examination of tooth enamel can confirm the age.

Last but not least, different races have different cranial features. Nasal aperture, eye orbit shape, subnasal prognathism are some of the features that can differ.

Further excavation must be done to determine for sure if there is more than one victim. At this stage it is also not possible to determine the gender, ethnicity and age of the victim.
Over time, certain changes might occur to the remains. A depression of the skull/broken bones could indicate death due to skull fracture but again, decomposition factors such as weather, soil chemical components, scavengers and insects must be taken into consideration. Or, the chin of a female (more rounded) can be mistaken for that of a male (more square) after decay over a long period.
The age can be determined by examining bone sizes and fusions/sutures. With age, joints or fontanels also change in size. Bone loss is significant of advanced age. Bone ossification examination also helps. Teeth erupt in a certain order and that also can greatly help determine the age. Additional information comes from examining the degree of root development deep within the jawbone. If wisdom teeth are present, individual was above 18. Finally, the microscopic examination of tooth enamel can confirm the age.

Last but not least, different races have different cranial features. Nasal aperture, eye orbit shape, subnasal prognathism are some of the features that can differ.




I like this - very resourceful and systemically approached!
ReplyDelete